
Audit committee reports present a periodic and annual picture of the financial reporting method, the audit process, data on the organization’s inside controls system and certainty that the organization is in agreement with laws and management. Have a look at the audit committee report templates provided down below and choose the one that best fits your purpose.



cdn.ymaws.com
File Format
hkexgroup.com
File Format committee annual report template" width="390" height="505" />
committee annual report template" width="390" height="505" />
eib.org
File Format
iosco.org
File Format
abengoa.com
File Format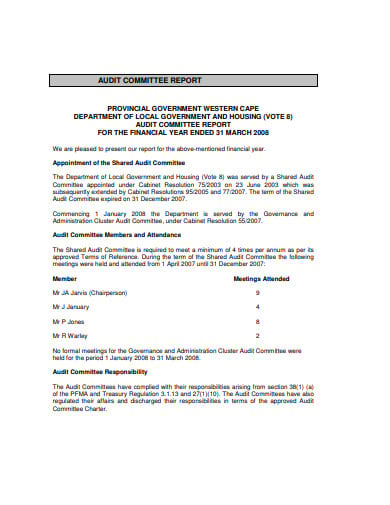
westerncape.gov.za
File Format committee annual report template" width="390" height="505" />
committee annual report template" width="390" height="505" />
agriculture.gov.ie
File Format
kasikornbank.com
File Format
corporate.amadeus.com
File Format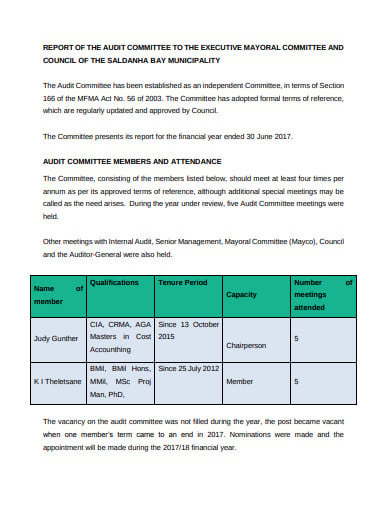
sbm.gov.za
File Format
threerivers.gov
File Format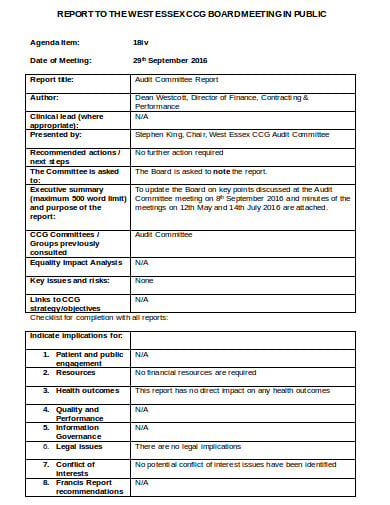
westessexccg.uk
One of the significant operating committees of an organization’s board of directors that is in management of managing financial reporting and disclosure is the audit committee. All U.S. publicly-traded organizations must manage an adequate audit committee in order to be recorded on a stock exchange.
The Companies Act needs at least one-third of the members of the audit committee to have academic essentials, or experience in finance, law, corporate governance, finance, accounting, business, manufacturing, public affairs or human resource management.
Benefits of audit committees are as follows:
It may increase the state of management accounting, as it is well placed to analyze inside functions. It should guide to better communication between the directors, external auditors, and management.
The ability to approach responsibilities with a questioning mind and a healthy sense of professional skepticism is priceless to an audit committee member. The requirement can rise to challenge the management team and keep them accountable, which can build difficult circumstances.
What is the Audit Planning Process?
stage consists of methods such as obtaining the perception of the customer and its business, making risk and materiality assessments, preparing an audit strategy. Performing the audit is defined as the method of gathering evidence.
The Committee’s mission is to supervise the accounting and financial reporting method of the organization, the audits of the organization’s financial statements, the appointment, independence, performance, and compensation of the sanctioned auditors comprising the Cost auditors, the production of inner auditors.
There is a collection of principles upon which auditing depends on, and these principles are solid and useful. They maintain the procedures and handles when maintaining an organization. It is necessary to get the scope of auditing like to give an organization’s management with data that the organization can then utilize to increase that organization’s performance. It not only assists management so that it can snap obstacles in the shoot, but also it tells management about fields in which it is already functioning well, but in which it could perform better.
4 steps to constituting a great audit committee are as follows:
An audit committee should function as the arm of the board of directors that guarantees decent financial management. As such, it’s an essential part of good governance, making it suitable for nonprofits of all dimensions. The committee’s job mostly comes down to oversight, which is normally concentrated on financial reporting, external and internal audit capacities, agreement with legal and regulatory necessities and the internal authorities over these sections.
The audit committee should take a much wider view, supervising the direction and uprightness of financial reporting, including building and executing accounting policies and inner controls to encourage good financial stewardship. The aim is to preserve the nonprofit’s assets, establish the dependability and efficiency of financial reporting, and diminish the risk of fraud.
The audit committee is accountable for hiring, remunerating and supervising external auditors and is therefore granted the auditors’ client. It should have constant communications with the auditors, including meetings to explain a work plan before the audit and to examine any findings before they’re given to the board.
Apart from the roles and duties described above, the committee must preserve its independence. That means audit committee members can’t endure any consulting, advisory or other compensatory fees from the company.